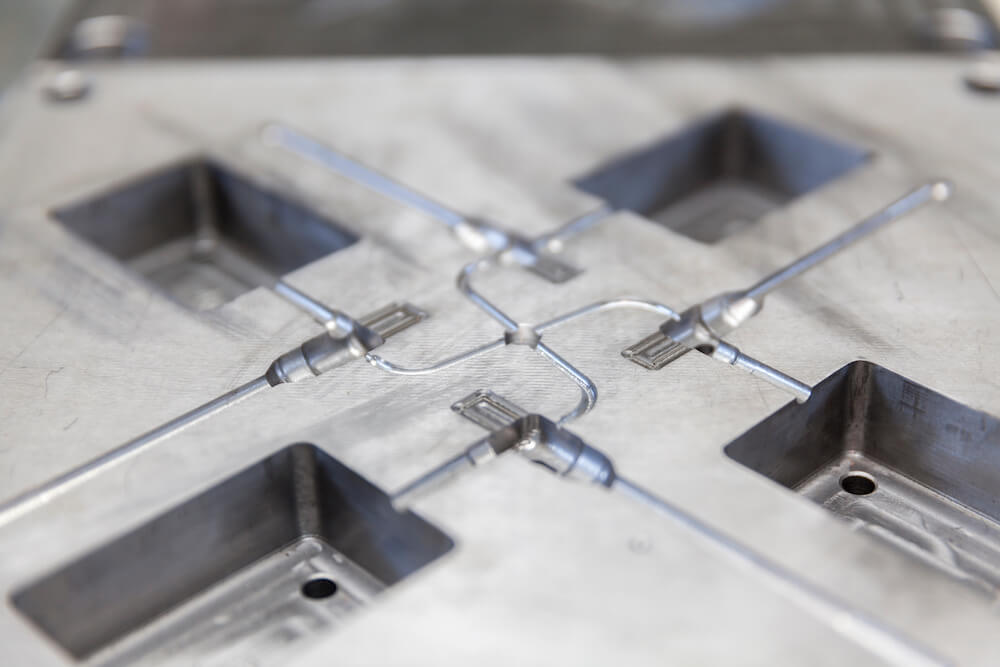
Injection molding is the primary manufacturing process for producing plastic parts across most industries. The process involves injecting molten plastic into a mold cavity, after which it cools and solidifies into the final part geometry. While full-scale production injection molds are meticulously engineered, less sophisticated prototype molds play an equally important role in bringing new plastic products to market.
Prototype injection molds allow engineers to iterate on part designs, evaluate manufacturability, and validate critical features before committing to high-volume production tooling. However, prototype tooling brings its own set of distinct challenges. Compared to production tooling, prototype molds typically demand faster turnaround, accommodate evolving specifications, and involve smaller production volumes–all under tight budget constraints.
Understanding Prototype Tooling in Injection Molding
Prototype tooling refers to injection molds fabricated for design verification, product testing, and low-volume part production during the early stages of product development. While full-scale production molds are optimized for producing hundreds of thousands of injection-molded parts, prototype molds have very different requirements and challenges.
Fundamentally, prototype injection molds prioritize fast turnaround, frequent design changes, and preliminary testing over production-level part quality, cycle life, and efficiency. Prototype molds may incorporate simplified mold features, easier-to-machine materials, and manually-actuated mold components to meet accelerated build schedules and early sampling needs.
Prototype injection molding is an intermediary step between rapid prototyping methods like 3D printing and full-blown production tooling. The role of prototype tooling is to provide engineers with a way to test molded part designs, experiment with various thermoplastics, refine critical features, and evaluate manufacturing processes before large dollar amounts are spent on multi-cavity steel production molds. Injection-molded prototype parts are equivalent to production parts and are used to validate fit, form, and function details that other prototyping methods cannot fully replicate.
Short test runs affirm molding process parameters, production feasibility, and highlight design improvements early when changes are less costly. Delivering this capability rapidly and cost-effectively relies on various emerging technologies covered throughout this article.
Challenges with Prototype Injection Molds
Constructing injection molds capable of producing prototype plastic parts introduces an array of distinct challenges that impact budget, schedule, performance, and quality. These prototyping hurdles require creative solutions.
Costs and Long Lead Times
Prototype injection molds frequently demand extensive custom machining to translate preliminary 3D CAD models into physical mold tooling. This relies on programming complex contours, acquiring special cutters, and securing skilled labor. As prototypes are typically low-volume assignments, these specialized machine shop tasks suffer from a lack of economies of scale, which can ratchet up costs. Allocating machining time also extends queue times and lead times.
Further, refining elaborate industrial molds with iterative geometry changes multiplies machining efforts. Updating prototypes to evolve part design aesthetics or improve molding fill involves re-programming, acquiring new cutters, and hours of additional precision machining time. These change orders add cost/schedule in a compounding manner. With production decisions looming, the long tail of custom mold modifications can cause delays.
Material Limitations
Standard mold alloys used for low-cost, faster prototyping work cannot withstand the prolonged duty cycles and abrasion seen in production molds. Their softer matrices enable faster machining but sacrifice durability. Running large prototype sampling programs deteriorates these less robust materials. Hardened tool steel alternatives that hold up remain costly for prototyping budgets.
Additionally, glass or carbon-reinforced thermoplastics help meet tighter dimensional tolerances but cause accelerated wear issues in lower-cost mold materials. Not validating higher-performance resins in prototypes delays learning and introduces uncertainties around molding production-intent components. Material caveats constrain realism.
Design Restrictions
By nature, prototype injection molds involve trade-offs between speed, cost, and capability relative to hardened production tooling. Certain challenging plastic part geometries involving tight tolerances, intricate details, micro features, and thin walls often exceed the machining limits or thermal properties of prototype alloys. Prototyping alternatives like additive manufacturing offer lower fidelity.
Compounding these inherent prototyping material limits and implementing iterative changes to refine molded component designs requires repeated extensive machining efforts. Updating a wall thickness or radius can involve re-programming coordinates, acquiring different tooling, and carving new geometries, often manually.
Limited Lifespan
In certain categories of prototype molds, operating lifetimes may only reach a few thousand cycles before wear, erosion, or dimensional instability sets in. Testing parameters across batches of thermoplastics, evaluating longer-term performance, or conducting pilot production runs may exceed these durability limits. This requires costly rebuilding efforts or scrapping initial tooling for hardened versions.
Aggressive Project Timelines
Despite the need for accelerated sampling of injection molded prototype components, constructing finely tuned mold tooling relies extensively on manual programming, machining, grinding, and polishing steps. Labor, equipment, and queue bottlenecks at specialized machine shops strain against compressed product development schedules.
Enter Protoshop Inc, your partner in transforming these challenges into opportunities. With our state-of-the-art injection molding services, we’re not just another link in the chain; we’re a solution provider dedicated to streamlining the path from prototype to production.
Overcoming Prototype Tooling Hurdles
While constructing short-run injection molds for prototyping introduces innate cost, time, capability, and durability constraints, a range of solutions now exist to better align with accelerated development schedules.
Bridging Technologies
Integrating bridging technologies, such as constructing mold cavities and core pins using 3D metal printing (DMLS) where possible, can significantly lower materials costs and lead times with more flexibility for adjustments. These components can help establish baseline validation data while final, more precise metal cavities and core pins are machined. Also, sections of molds with fine detail can be inserted with stainless steel; only the most critical sections of the mold need to be machined into the hardened metal at the required slower pace.
Advanced Machining Methods
Recent specialized machining methods like high-speed graphite milling and hard milling markedly improve the machinability of hardened mold alloys like P20 steel and H13 tool steel. This expands complexity capabilities and boosts multi-axis precision. Adapting small-diameter tapered end mills coupled with high RPM machining facilitates faster, more affordable production of higher-density molds with greater sophistication to meet stringent prototype requirements. Automating CAD-to-path programming and integrating robotic cutter changers also accelerates turnaround by reducing manual programming bottlenecks.
Modular Standardized Components
Rather than fully custom projects, integrating modular, standardized mold bases, plates, inserts, components, and accessories into prototypes streamlines fabrication while maintaining quality. Cataloged interchangeable pieces with production-level durability and consistency integrate quickly via dowels and bolts to enable more robust sampling capabilities. They also seamlessly transfer into full mold builds, reducing scrapped efforts.
Proactive Design Strategies
Simulating manufacturability digitally via mold flow analysis and structural mechanics tools during the CAD design phase guides engineers toward viable prototype geometries proactively. This prevents extensive physical trial-and-error machining that burns budget. Building awareness of future machining improvements into progressive models and designing for forthcoming material advances also extends usefulness and lifecycles.
Specialized Vendors and Services
Strategically outsourcing to specialized prototype tooling partners combines the upside of emerging methods above while leveraging process expertise honed over rapid product launch programs. Tailored, hybrid solutions integrate both bridge tooling and machined components to accelerate injection molding prototypes, meeting budget, quality, and lead time realities under one roof.
Let Protoshop Deliver High-Quality, Rapid Prototype Molds and Parts
Constructing reliable prototype injection molds that yield quality plastic components on accelerated timelines poses innate technical and process hurdles. From custom machining challenges to iterative design changes, inherent prototyping constraints frequently yield frustrating outcomes that derail development initiatives and delay market launch decisions.
Navigating the innovation roadblocks in prototype tooling for injection molding becomes seamless when partnering strategically with specialist vendors renowned for refining and sampling plastic part designs. Protoshop Inc., with its 25-plus years of dedicated service in high-mix medical prototype mold fabrication and molding, stands out in this domain. Our advanced digital workflow enables us to deliver high-fidelity, short-run injection molds within five days or less, regardless of the complexity of geometries. We embrace the challenging projects that others shy away from, reinforcing our reputation for excellence and reliability.
At Protoshop Inc., we pride ourselves on our precision and commitment to large-scale prototype tooling for injection molding. Our use of cutting-edge technology and stringent quality control processes ensures that we consistently produce parts with superior accuracy, setting new industry benchmarks and eclipsing our competitors. Our profound expertise allows us to navigate the intricate challenges of large-scale prototyping, guaranteeing that our clients receive meticulously crafted components that align perfectly with their precise specifications.
Our combination of purpose-built proprietary methods, interactive consultations, and production-mirrored quality standards de-risks prototyping. As true prototyping experts, Protoshop enables customers to avoid prohibitive prototype expenses, extended lead times, and quality uncertainty to accelerate plastic products to market. Reach out to our team today.