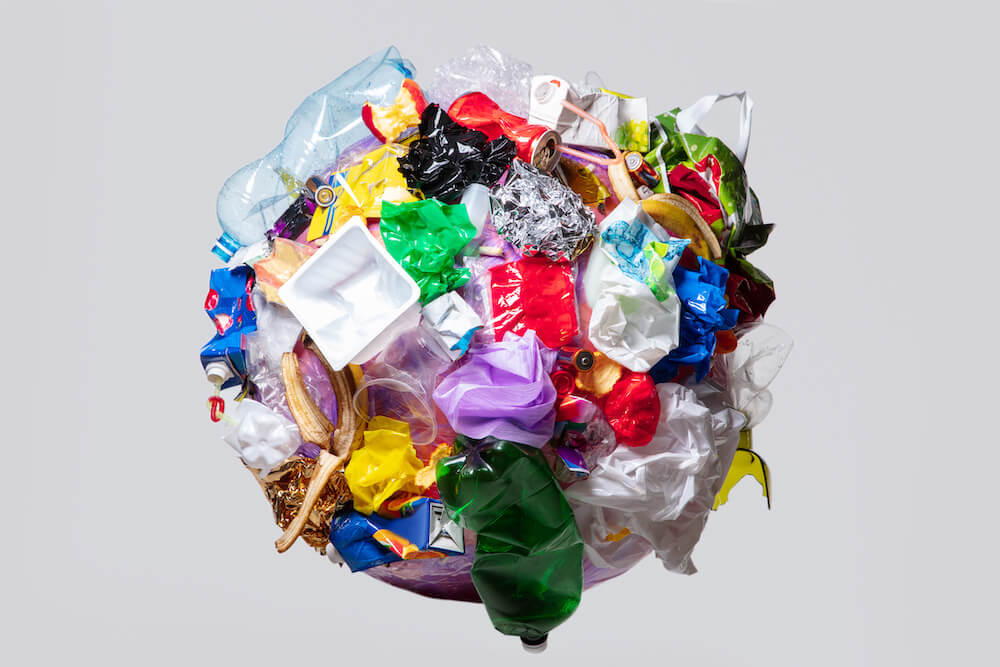
As industries like Protoshop strive to reduce the environmental impact of waste plastic, the use of recyclable materials in prototype injection molding must be seriously considered.
While the benefits of using recyclable materials seem clear, an injection mold with recycled plastic comes with its own set of unique challenges.
Types of Recyclable Materials: PIR and PCR
Regrind, or PIR (Post Industrial Regrind), is scrap plastic that has been recaptured by a manufacturer from the injection molding process. Regrind includes parts that were rejected due to blemishes or short shots, gate and runner systems molded as part of channeling the plastic from the screw barrel to the mold cavity, and parts that were used for verification/validation processes and cannot be sold. These plastic materials are ground into small pieces in preparation for being reintroduced to the injection molding process.
Post-consumer regrind (PCR) is recycled plastic that has been used by the consumer and reclaimed. PCR is collected from recycling programs and manufacturing plants around the world. These plastics require additional sorting, cleaning, and processing to eliminate contaminants and ensure proper categorization by plastic-type before being ground into small pieces suitable for injection molding.
Since the heating and molding processes alter the physical performance properties of plastics, regrind plastics can no longer considered “virgin” materials. Typically, virgin materials are mixed with PIR at a 75-25 ratio to mitigate the decrease in plastic material performance, but this ratio can be application specific. Medical devices, for example, must always use virgin plastic, while other consumer parts, such as drink coasters, could use 100% regrind.
Material Quality Variability: The Inconsistent Nature of Recycled Plastics
One of the primary challenges in injection molding recycled plastics is the inconsistency in material quality. Unlike virgin plastics, which have predictable and uniform properties, recycled materials can vary significantly from batch to batch. This variability can lead to inconsistencies in the final product, affecting everything from dimensional accuracy to surface finish due to:
- Fluctuating melt flow indices, leading to inconsistent fill patterns
- Varying shrinkage rates, causing dimensional inaccuracies
- Inconsistent color distribution in the final part
Mitigating Strategies
To address this challenge in injection molding, there must be:
- Comprehensive material testing before each production run
- Blending of multiple batches to achieve more consistent properties
- Dynamic adjustment of injection molding parameters based on material characteristics
Contamination: The Hidden Threat in Recycled Plastics
Another significant challenge in using recyclable materials for injection molding is contamination. Recycled plastics often contain impurities from their previous life or the recycling process.
Common Contaminants
- Metal particles from labels or caps
- Other plastic types mixed in during the recycling process
- Organic residues from food packaging
Impact on Injection Molding
These contaminants can wreak havoc on the injection molding process, leading to:
- Clogged nozzles and damaged equipment
- Weak points or voids in the final part
- Surface defects and blemishes
Managing Contamination
Contamination of material must be managed through:
- Implementing advanced filtration systems in our prototype injection molding machines
- Partnering with reliable suppliers who provide high-quality recycled materials
- Utilizing melt filtration techniques to remove contaminants during the molding process
Material Degradation: The Silent Performance Killer
Recycled plastics often undergo multiple heat cycles during their lifetime, leading to thermal degradation. This degradation can significantly impact the material’s mechanical properties, posing challenges for injection molding.
Effects of Degradation
- Reduced tensile strength and impact resistance
- Increased brittleness
- Changes in viscosity affecting flow behavior during injection
Addressing Degradation in Product Development
To ensure plastic components meet the required performance standards, molders must:
- Conduct thorough material analysis to assess the level of degradation
- Blend recycled materials with virgin plastics to improve overall properties
- Adjust processing parameters to accommodate for changes in material behavior
Processing Issues: Navigating the Complexities of Recycled Materials
The varying melt flow characteristics and viscosities of recycled materials can complicate the injection molding process. These differences can lead to processing issues that affect the quality and consistency of the final component.
Challenges in Processing
- Inconsistent filling of mold cavities
- Difficulty in achieving proper packing pressure
- Increased cycle times due to processing adjustments
Optimizing the Process
Experienced molders can develop expertise in handling these processing challenges by:
- Utilizing advanced simulation software to predict and optimize flow behavior
- Implementing adaptive process control systems that adjust in real-time
- Designing molds with enhanced venting and cooling to accommodate processing variabilities
Additives: Enhancing Performance of Recycled Materials
Additives can help overcome some inherent limitations of recycled materials in injection molding, improving material performance and processability.
Common Additives for Recycled Materials:
- Stabilizers to prevent further degradation
- Compatibilizers to improve the blend of different recycled plastics
- Flow enhancers to improve processability
Balancing Act
While additives can significantly improve material properties, their use must be carefully balanced. Too much can affect the recyclability of the final product, while too little may not provide the desired improvements.
Additives can be successfully used to:
- Improve the impact strength of recycled PP in automotive prototypes
- Enhance the flow characteristics of recycled PET in thin-walled packaging
- Stabilize recycled HDPE for outdoor products
The Road Ahead: Embracing Sustainability Using Prototype Injection Molding
As we navigate the challenges of using recyclable materials in injection molding, the benefits far outweigh the difficulties.
Key Takeaways
- Material quality variability requires robust testing and adjustment protocols.
- Contamination management is essential for maintaining product quality and equipment longevity.
- Understanding and addressing material degradation is essential to ensuring molded part performance.
- Processing challenges can be overcome with advanced technology and expertise.
- Careful use of additives can significantly enhance the properties of recycled materials.
At Protoshop, we’re committed to pushing the boundaries of sustainable manufacturing and continuously innovating to overcome these hurdles by manufacturing prototypes in recyclable materials for your evaluation.
As we refine our processes and expand our capabilities, we invite you to join us on this journey towards more sustainable manufacturing. Whether you’re looking to develop a new product or improve an existing one, Protoshop is here to help you navigate the complexities of using recyclable materials in your prototype injection molding projects.
Ready to take your prototyping to the next level with sustainable materials? Contact Protoshop today, and let’s work together to bring your ideas to life—responsibly and innovatively.